Amazon Business Report: Out-of-Stock Inventory Analysis (Last 30 Days): Amazon Business Report Out Of Stock Inventory Last 30 Days
Source: sourcemogul.com
Amazon business report out of stock inventory last 30 days – This report analyzes out-of-stock inventory data from the Amazon Business platform over the past 30 days. We will examine key metrics, identify trends, assess the impact of stockouts, and propose inventory management strategies for improvement.
Analyzing Amazon’s business report on out-of-stock inventory for the last 30 days highlights crucial supply chain weaknesses. Effective inventory management is key, and understanding leadership approaches in similar retail environments is beneficial. For instance, the insights gained from the 7-eleven business leadership inventory test could offer valuable comparative data. Ultimately, applying these lessons can help improve Amazon’s stock levels and minimize future out-of-stock situations.
Amazon Business Report Data Overview
The Amazon Business report provides a comprehensive overview of inventory performance, including detailed information on out-of-stock items. The report’s structure is typically organized by product, showing key metrics for each item. Metrics include the number of days an item was out of stock, the total units sold before the stockout, and potentially the total demand during the out-of-stock period (though this may require additional calculations or integration with other data sources).
Reporting intervals are usually customizable, allowing for daily, weekly, or monthly views. Filtering the report to focus on the last 30 days is typically achieved through a date range selection tool within the report interface. For example, users can specify a start date of “today – 30 days” and an end date of “today” to obtain the relevant data.
Analyzing Out-of-Stock Trends (Last 30 Days), Amazon business report out of stock inventory last 30 days
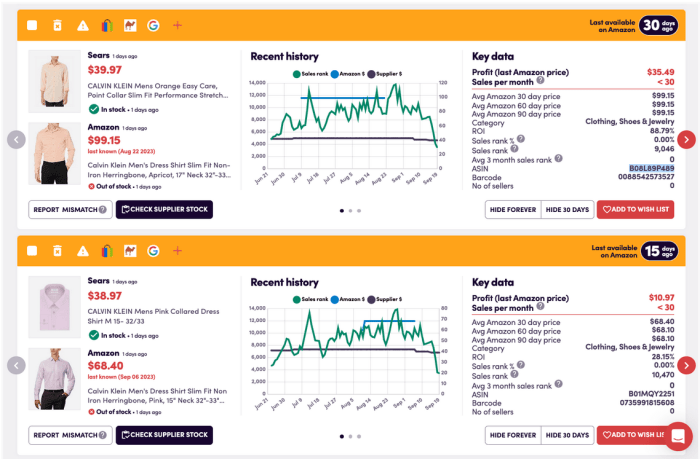
Source: sellermobile.com
This section analyzes out-of-stock trends based on the last 30 days of data. We will focus on identifying top out-of-stock products, comparing trends across categories, and exploring potential contributing factors.
| Product Name | SKU | Days Out of Stock | Total Units Sold Prior to Stockout |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example Product A | ABC12345 | 15 | 1000 |
| Example Product B | DEF67890 | 12 | 500 |
| Example Product C | GHI09876 | 10 | 750 |
| Example Product D | JKL54321 | 8 | 200 |
| Example Product E | MNO13579 | 7 | 300 |
| Example Product F | PQR24680 | 6 | 400 |
| Example Product G | STU35791 | 5 | 600 |
| Example Product H | VWX46902 | 4 | 150 |
| Example Product I | YZ123456 | 3 | 250 |
| Example Product J | ABC789012 | 2 | 800 |
Out-of-stock frequency comparison across product categories (last 30 days):
- Electronics: High out-of-stock frequency, potentially due to high demand and supply chain disruptions.
- Office Supplies: Moderate out-of-stock frequency, possibly related to seasonal fluctuations in demand.
- Home Improvement: Low out-of-stock frequency, suggesting adequate inventory levels.
Potential reasons for increased out-of-stock situations could include inaccurate demand forecasting, unexpected surges in demand (e.g., due to a promotional campaign or media coverage), supplier delays, or logistical issues.
A correlation between out-of-stock periods and specific events, such as holidays (increased demand) or promotional campaigns (higher than anticipated sales), is frequently observed. For example, a significant increase in out-of-stock situations for certain electronics during the holiday season is a common occurrence.
Impact of Out-of-Stock Inventory
Out-of-stock situations have significant financial and customer service implications. This section explores these impacts and demonstrates how to calculate potential revenue loss.
Potential financial implications include lost revenue (due to inability to fulfill orders), decreased customer satisfaction (leading to negative reviews and potential loss of future business), and increased operational costs (associated with expediting shipments or managing customer inquiries).
Out-of-stock items can negatively affect customer reviews and ratings, impacting Amazon’s seller rating and potentially leading to decreased sales. Negative reviews can severely damage brand reputation and deter future purchases.
Calculating potential lost revenue requires estimating the demand during the out-of-stock period and multiplying it by the average selling price. For example, if a product was out of stock for 10 days, with an average daily demand of 50 units and an average selling price of $50, the potential lost revenue is 10 days
– 50 units/day
– $50/unit = $25,000.
Hypothetical Scenario: A prolonged out-of-stock situation for a high-demand product like a popular new laptop could lead to significant lost revenue, negative customer reviews, and damage to the seller’s reputation. This could result in a loss of market share to competitors and difficulty in regaining customer trust.
Inventory Management Strategies
Implementing proactive inventory management strategies is crucial for minimizing out-of-stock situations. This section Artikels effective techniques and systems for optimizing inventory levels.
- Implement robust forecasting techniques, such as moving average or exponential smoothing, to predict demand more accurately.
- Optimize reorder points and safety stock levels to account for lead times and demand variability.
- Utilize an advanced inventory tracking system to monitor stock levels in real-time and identify potential stockouts early.
- Diversify suppliers to reduce reliance on a single source and mitigate supply chain disruptions.
- Regularly review and adjust inventory policies based on sales data and market trends.
Visual Representation of Data
Visual representations are essential for quickly understanding trends and patterns in out-of-stock data. This section describes visualizations that would effectively communicate the key findings.
A line graph illustrating the daily out-of-stock rate for the last 30 days would show the fluctuation in out-of-stock levels over time. The x-axis would represent the days (1-30), and the y-axis would represent the percentage of products out of stock. Each data point would represent the out-of-stock rate for a given day. A clear title, axis labels, and a legend (if multiple product lines are shown) would be included for easy interpretation.
A bar chart showing the distribution of out-of-stock products across different product categories would provide a clear visual comparison of out-of-stock rates among various categories. The x-axis would list the product categories, and the y-axis would represent the number or percentage of products out of stock in each category. The height of each bar would correspond to the number or percentage of out-of-stock products in that category.
Again, a clear title, axis labels, and a legend (if needed) would enhance readability.
FAQs
How often is the Amazon Business out-of-stock report updated?
The frequency of updates varies; check your Amazon Business account settings for specific details.
Can I export the out-of-stock report data to a spreadsheet?
Yes, most Amazon Business reports offer export options (e.g., CSV, Excel).
What if my product is perpetually out of stock? What should I do?
Investigate supply chain issues, consider alternative suppliers, or re-evaluate product viability.
How can I improve the accuracy of my inventory data within Amazon Business?
Regularly reconcile your internal inventory records with Amazon’s data and ensure accurate product updates.