Alaska Business Inventory Tax: An Overview
The Alaska Business Inventory Tax is a levy imposed on businesses operating within the state, based on the value of their taxable inventory held within Alaska at a specific point in time. Understanding this tax is crucial for businesses to ensure compliance and manage their financial obligations effectively. This overview will explore the key aspects of this tax, from its purpose and scope to its calculation, payment, and potential future developments.
Overview of the Alaska Business Inventory Tax
Source: businesssearch.org
The Alaska business inventory tax aims to generate revenue for the state government. Its scope encompasses a wide range of businesses, as detailed below. The tax’s history reflects adjustments over time to reflect economic changes and legislative priorities. While specific historical data requires referencing official state records, it’s understood that the tax has undergone revisions to its rates and exemptions throughout its existence, reflecting evolving economic conditions and policy decisions.
Types of Businesses Subject to the Tax
The Alaska business inventory tax applies to various business types, primarily those holding inventory for sale in the ordinary course of business. This includes retailers, wholesalers, manufacturers, and other businesses with significant inventory holdings. Specific exemptions might exist for certain industries or types of inventory, requiring careful review of the relevant state regulations.
Taxable Inventory
Determining what constitutes taxable inventory under Alaskan law hinges on whether the goods are held for sale in the ordinary course of business. Raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods generally fall under this category. The valuation methods used to assess taxable inventory are crucial in determining the tax liability. Specific exceptions and exemptions might exist for certain types of inventory, such as perishable goods or items designated for specific purposes.
Inventory Valuation Methods

Source: managebusiness.org
| Valuation Method | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | The original cost of acquiring the inventory. | Simple and objective. | May not reflect current market value. |
| Market Value | The current market price of the inventory. | Reflects current economic conditions. | Can be subjective and difficult to determine. |
| Lower of Cost or Market (LCM) | The lower value between cost and market value. | Provides a conservative valuation. | May result in lower tax liability than the actual value. |
Exceptions and Exemptions
Specific exceptions and exemptions may apply to certain inventory items. For example, certain agricultural products or goods destined for export might qualify for exemptions. Businesses should consult the official Alaska Department of Revenue guidelines for a comprehensive list of exceptions and exemptions.
Tax Calculation and Reporting
Calculating the Alaska business inventory tax involves determining the value of taxable inventory using the chosen valuation method and applying the relevant tax rate. Applicable deductions or credits might reduce the overall tax liability. The tax return must be filed by the specified deadline, with all necessary documentation.
Tax Rates and Deductions
The tax rate for the Alaska business inventory tax is subject to change based on legislative action. Businesses should consult the official state resources for the most up-to-date tax rate information. Specific deductions or credits might be available, depending on the type of business and inventory held. These deductions may include those related to certain inventory losses or other specific business circumstances.
Sample Tax Return Form
A simplified representation of a tax return form would include fields for business name, address, tax year, total inventory value (using the chosen valuation method), applicable deductions, calculated tax liability, and payment information. The actual form provided by the Alaska Department of Revenue will contain more detailed information and fields.
Tax Payment and Penalties
The Alaska business inventory tax can be paid through various methods, including online payments, mail, and potentially through designated financial institutions. Late payment or non-compliance can result in penalties, including interest charges and potential legal actions. Businesses can appeal tax assessments or penalties through the established channels within the Alaska Department of Revenue.
Common Reasons for Tax Audits and Penalties, Alaska business inventory tax
- Inaccurate reporting of inventory value.
- Failure to file the tax return by the deadline.
- Incorrect application of valuation methods.
- Lack of proper documentation to support claimed deductions.
- Non-payment or late payment of taxes.
Comparison with Other States
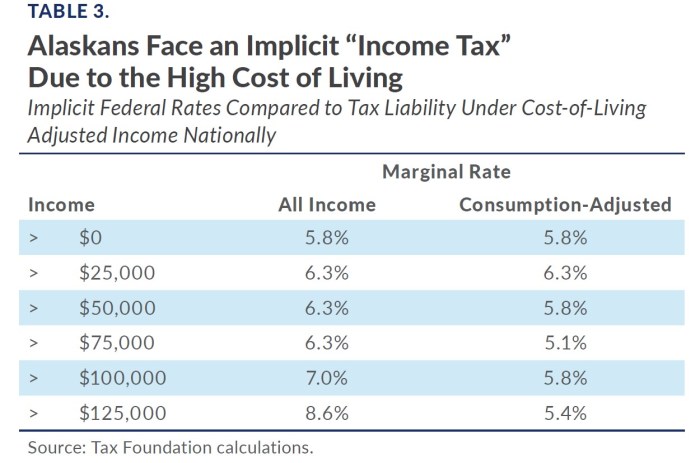
Source: alaskapolicyforum.org
Comparing the Alaska business inventory tax to similar taxes in other states requires analyzing differences in tax rates, assessment methods, and reporting requirements. For example, some states might have higher or lower tax rates, different valuation methods, or more stringent reporting requirements. These differences significantly impact businesses operating in multiple states, requiring careful tax planning and compliance across various jurisdictions.
Impact on Businesses
The Alaska business inventory tax affects businesses’ profitability, investment decisions, and job creation. High tax rates can reduce profit margins and discourage investment. Businesses often adapt by optimizing inventory management, negotiating with suppliers, or seeking tax-efficient strategies to mitigate the tax burden. For instance, a business might implement just-in-time inventory management to reduce the overall value of inventory held at any given time.
Future of the Alaska Business Inventory Tax
The future of the Alaska business inventory tax may involve potential changes or reforms driven by economic conditions, legislative priorities, and ongoing debates regarding the tax’s effectiveness and fairness. Discussions around simplification, rate adjustments, or even potential replacement with alternative tax structures are possible scenarios for future tax policy.
Questions and Answers: Alaska Business Inventory Tax
What types of businesses are exempt from the Alaska Business Inventory Tax?
Specific exemptions exist, often for certain non-profit organizations or businesses meeting specific criteria. Consult the official Alaska Department of Revenue website for the most up-to-date exemption details.
What happens if I fail to pay the Alaska Business Inventory Tax on time?
Alaska’s business inventory tax can be complex, particularly when dealing with significant sales. Understanding how the tax applies to large transactions is crucial for accurate reporting. For instance, consider a scenario where a business tax payer sells inventory for 80000 ; this sale would likely trigger specific reporting requirements under the Alaska business inventory tax system, necessitating careful record-keeping and potentially impacting the overall tax liability.
Late payment penalties are applied, and interest may accrue on the outstanding balance. Severe non-compliance can lead to further penalties and potential legal action.
Where can I find the official forms and instructions for filing the Alaska Business Inventory Tax return?
The Alaska Department of Revenue website provides access to all necessary forms, instructions, and relevant publications.
Can I appeal a tax assessment or penalty?
Yes, there’s a formal appeals process. The specifics of this process are detailed on the Alaska Department of Revenue website. It’s crucial to follow the Artikeld procedures for a successful appeal.