Economic Impact of a $2 Billion Inventory Increase
A 2 billion increase in business inventories – A $2 billion increase in business inventories signifies a notable shift in the economic landscape, impacting various sectors and influencing overall growth. This increase reflects a complex interplay of factors, from supply chain adjustments to shifts in consumer demand. Understanding its implications is crucial for businesses and policymakers alike.
Effects on GDP Growth
A $2 billion increase in business inventories contributes positively to Gross Domestic Product (GDP) calculations in the short term. Inventories are considered a component of investment spending within the GDP equation. However, this positive impact is temporary. If the inventory build-up reflects overproduction or a failure to anticipate a slowdown in demand, the subsequent need to reduce inventory levels could lead to a contraction in GDP in future quarters.
For example, a similar situation occurred in the early 2020s, where initial inventory stockpiling later contributed to economic slowdowns as businesses worked to liquidate excess goods.
Ripple Effects on Consumer Spending and Investment
Source: cloudfront.net
The impact on consumer spending and investment depends largely on the reasons behind the inventory increase. If the increase is due to anticipated future demand, it might lead to increased production and employment, potentially stimulating consumer spending. Conversely, if the increase stems from supply chain disruptions or overproduction, it could signal a weakening of consumer demand, leading to price reductions and potentially dampening future investment.
A scenario where businesses are forced to discount goods to clear excess inventory could lead to lower profit margins and reduced investment in future expansion.
Impact Across Economic Sectors
The impact of the inventory increase varies significantly across sectors. Industries with high inventory turnover, such as retail and consumer goods, may experience greater pressure to clear excess stock through discounting, impacting profit margins. Conversely, industries with longer production cycles and less price-sensitive goods, like manufacturing of capital equipment, may be less immediately affected. The technology sector, known for its rapid innovation cycles, might experience more pronounced impacts if technological obsolescence quickly renders a portion of the increased inventory less valuable.
Hypothetical Scenario: Rapid Inventory Decrease, A 2 billion increase in business inventories
Imagine a scenario where the $2 billion inventory increase is followed by a rapid and unexpected decrease. This could be triggered by a sudden drop in consumer demand or a shift in market preferences. The subsequent decrease would likely lead to a reduction in production, layoffs, and a contraction in economic activity. Businesses would face significant losses due to write-downs of unsold inventory, and the ripple effects could negatively impact consumer confidence and overall economic growth.
A $2 billion increase in business inventories raises concerns about potential overstocking. Understanding the implications requires careful analysis, and utilizing tools like the five key inventory ratios outlined in this helpful guide: 5 inventory ratios to measure your business performance tradegeckotradegecko can provide valuable insights. Properly interpreting these ratios is crucial for effectively managing the recent inventory surge and avoiding future imbalances.
This scenario highlights the inherent risks associated with significant inventory fluctuations.
Causes of the $2 Billion Inventory Increase
Several factors contribute to a significant increase in business inventories. These can be broadly categorized into supply-side issues, demand-side expectations, and macroeconomic influences.
Potential Reasons for Inventory Increase
A combination of factors likely contributed to the $2 billion increase. Supply chain disruptions, aiming to mitigate future shortages, increased production in anticipation of robust demand, and strategic inventory management in the face of macroeconomic uncertainty are all plausible explanations.
Role of Macroeconomic Factors
Interest rates and inflation play a crucial role. High interest rates increase borrowing costs, potentially discouraging businesses from investing in increased production and inventory. Inflation can lead to businesses stockpiling goods to protect against future price increases, contributing to the inventory surge. Conversely, low interest rates can encourage businesses to increase production and hold larger inventories.
Industries Most Affected
Industries with long lead times in production or those facing significant supply chain challenges are more likely to experience significant inventory build-ups. Examples include automotive manufacturing (due to semiconductor shortages), electronics manufacturing, and certain segments of the food and beverage industry (due to agricultural supply disruptions).
Categorization of Potential Causes
| Cause Category | Specific Example | Impact on Inventory | Potential Long-Term Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supply Chain Disruptions | Semiconductor shortage impacting automotive production | Increased inventory of unfinished vehicles | Potential for increased production costs and pricing pressure |
| Increased Production | Anticipation of strong holiday sales in retail | Higher-than-usual inventory levels before peak season | Potential for increased sales and profitability if demand materializes |
| Anticipated Demand | Government stimulus leading to expected increase in consumer spending | Preemptive stockpiling of goods to meet potential surge in demand | Potential for strong sales growth if expectations are met |
| Macroeconomic Factors | High inflation leading to price uncertainty | Increased inventory as a hedge against future price increases | Potential for higher profit margins if inflation continues; potential for losses if inflation subsides |
Industry-Specific Analysis of Inventory Increase
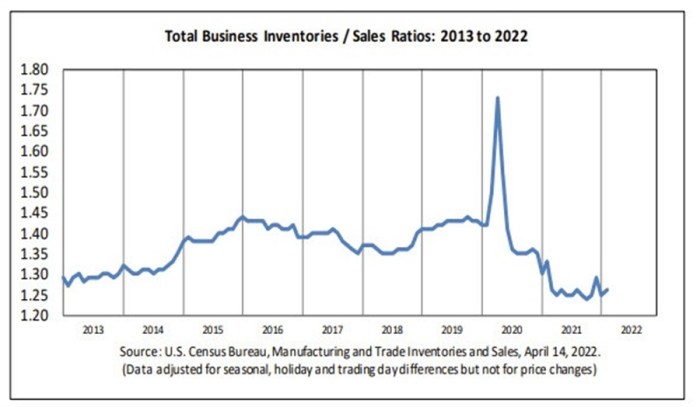
Source: forexlive.com
The $2 billion inventory increase affects different industries in unique ways, necessitating varied responses and strategic adjustments.
Impact on Specific Industries
The manufacturing sector might experience increased warehousing costs and potential for obsolescence. Retail businesses could face pressure to discount excess inventory, impacting profit margins. The technology sector may encounter challenges due to rapid product cycles and the risk of inventory becoming obsolete.
Inventory Management Strategies
Different industries employ varying strategies. Retailers may focus on aggressive promotional campaigns to clear excess inventory. Manufacturers might adjust production schedules to align with demand forecasts. Technology companies may prioritize rapid product innovation to minimize obsolescence risks.
Potential for Price Adjustments
High inventory levels generally put downward pressure on prices. Retailers and consumer goods companies are likely to resort to discounting to clear excess stock, while manufacturers might offer volume discounts to wholesalers and distributors. The extent of price adjustments will vary depending on industry-specific factors, including price elasticity of demand and competitive landscape.
Challenges and Opportunities
- Manufacturing: Challenges include increased warehousing costs and risk of obsolescence; opportunities include potential for increased production efficiency and economies of scale.
- Retail: Challenges include pressure to discount and reduced profit margins; opportunities include increased sales volume and potential for market share gains.
- Technology: Challenges include rapid product obsolescence and intense competition; opportunities include faster innovation cycles and the potential for capturing early-adopter markets.
Financial Implications for Businesses
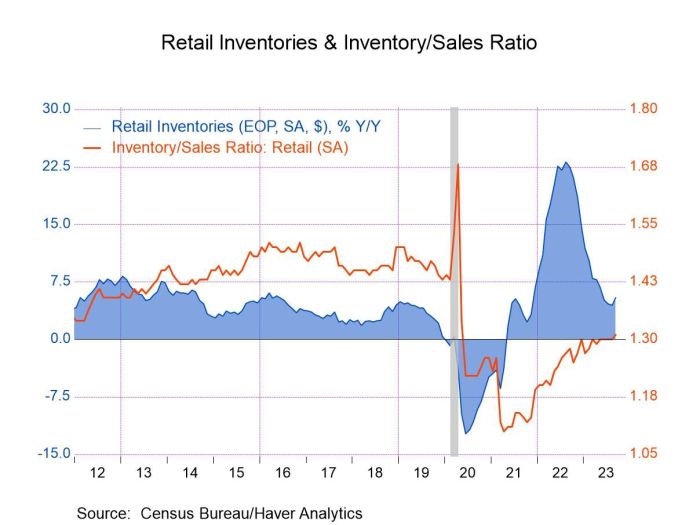
Source: amazonaws.com
The inventory increase significantly impacts businesses’ financial health, influencing their balance sheets, cash flow, and profitability.
Impact on Balance Sheets and Cash Flow
The increase ties up significant capital, reducing liquidity and potentially affecting the company’s debt-to-equity ratio. Cash flow is impacted by increased warehousing and insurance costs, as well as potential write-downs if inventory becomes obsolete.
Impact on Profitability and ROI
Increased inventory holding costs, including storage, insurance, and potential obsolescence, directly reduce profitability. Return on investment (ROI) is negatively affected as capital is tied up in inventory rather than being deployed in more profitable ventures.
Financial Strategies for Inventory Management
Businesses can employ various strategies, including just-in-time inventory management, improved demand forecasting, and strategic partnerships with suppliers to mitigate the financial risks associated with excessive inventory. They can also explore financing options to manage the increased inventory costs.
Financial Implications Summary
| Financial Metric | Potential Impact | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Balance Sheet | Increased current assets (inventory), potentially reduced liquidity | Improved inventory management, optimized production scheduling |
| Cash Flow | Reduced cash flow due to increased holding costs | Efficient warehousing, inventory financing options |
| Profitability | Reduced profit margins due to increased costs and potential write-downs | Demand forecasting, strategic pricing |
| ROI | Lower ROI due to capital tied up in inventory | Improved inventory turnover, diversification of investments |
Visual Representation of Inventory Trends
Effective visualizations are crucial for understanding the dynamics of inventory levels.
Historical Inventory Trend Chart
A line chart depicting historical inventory levels over, say, the past five years, would provide context. The x-axis would represent time (years and months), and the y-axis would show inventory value (in billions of dollars). The chart would illustrate the overall trend leading up to the $2 billion increase, highlighting any seasonal fluctuations or significant changes in inventory levels.
Data points would represent monthly or quarterly inventory values.
Inventory Levels vs. Sales
A scatter plot would effectively show the relationship between inventory levels and sales over a 12-month period following the $2 billion increase. The x-axis would represent inventory levels, and the y-axis would show sales figures. The plot would reveal whether the inventory increase correlates with increased sales or whether it reflects overstocking. A trend line could be added to visualize the overall relationship.
Visualization of Financial Metrics
A combination chart, possibly a bar chart overlaid with a line chart, could illustrate the impact of the inventory increase on key financial metrics such as profitability, cash flow, and ROI over time. The bar chart could represent the inventory levels, while the line charts would depict the trends in profitability, cash flow, and ROI. This would provide a comprehensive overview of the financial implications of the inventory increase.
User Queries: A 2 Billion Increase In Business Inventories
What are the potential downsides of such a large inventory increase?
Potential downsides include increased storage costs, potential for obsolescence of goods, tying up capital that could be used elsewhere, and the risk of needing to discount goods to clear excess stock.
How might this affect smaller businesses compared to larger corporations?
Smaller businesses may have less flexibility to absorb the costs associated with increased inventory, potentially impacting their cash flow and profitability more severely than larger corporations with greater financial resources.
Could this inventory increase be a sign of future economic slowdown?
It’s a possibility. A large inventory build-up could indicate that businesses are overestimating future demand. If demand doesn’t materialize, this could lead to a slowdown as businesses reduce production and potentially lay off workers.
What role does government policy play in influencing inventory levels?
Government policies, such as interest rate adjustments and tax incentives, can significantly impact business investment and production, indirectly influencing inventory levels. For example, higher interest rates can discourage borrowing and investment, leading to lower inventory levels.